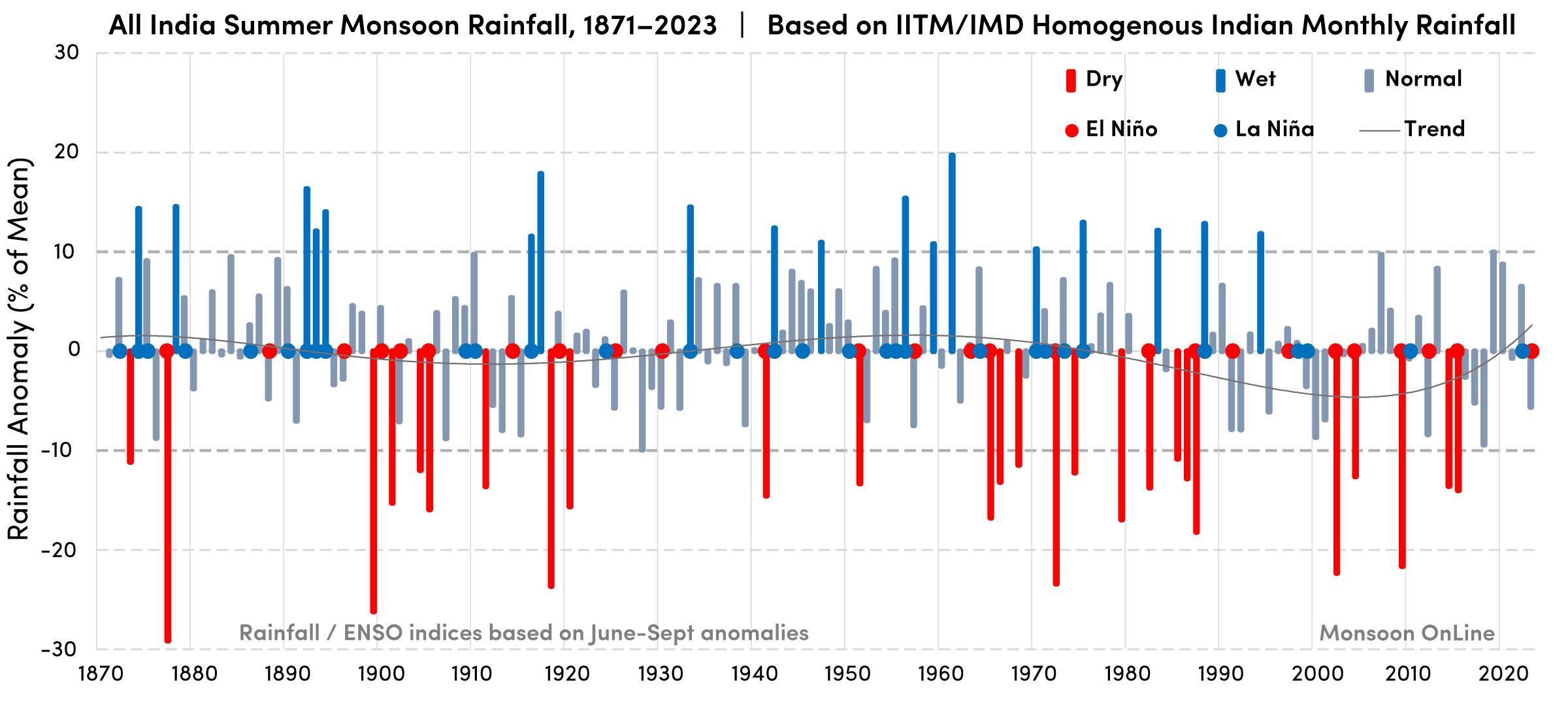
The All-India area-weighted mean summer monsoon rainfall (AISMR), based on a homogeneous rainfall data set of 306 rain gauges in India, developed by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, is widely considered as a reliable index of summer monsoon activity over the Indian region. The time series evolution of AISMR anomalies is expressed as percentage departures from its long-term mean over 1871-2020.
Drought years (below -10% departure) are marked in red color and flood years (above 10% departure) are marked in dark blue color. El Niño and La Niña conditions for the summer season are marked using red and blue dots.
Download the data for the Monsoon Interannual Timeseries: [iitm_aismr.txt]
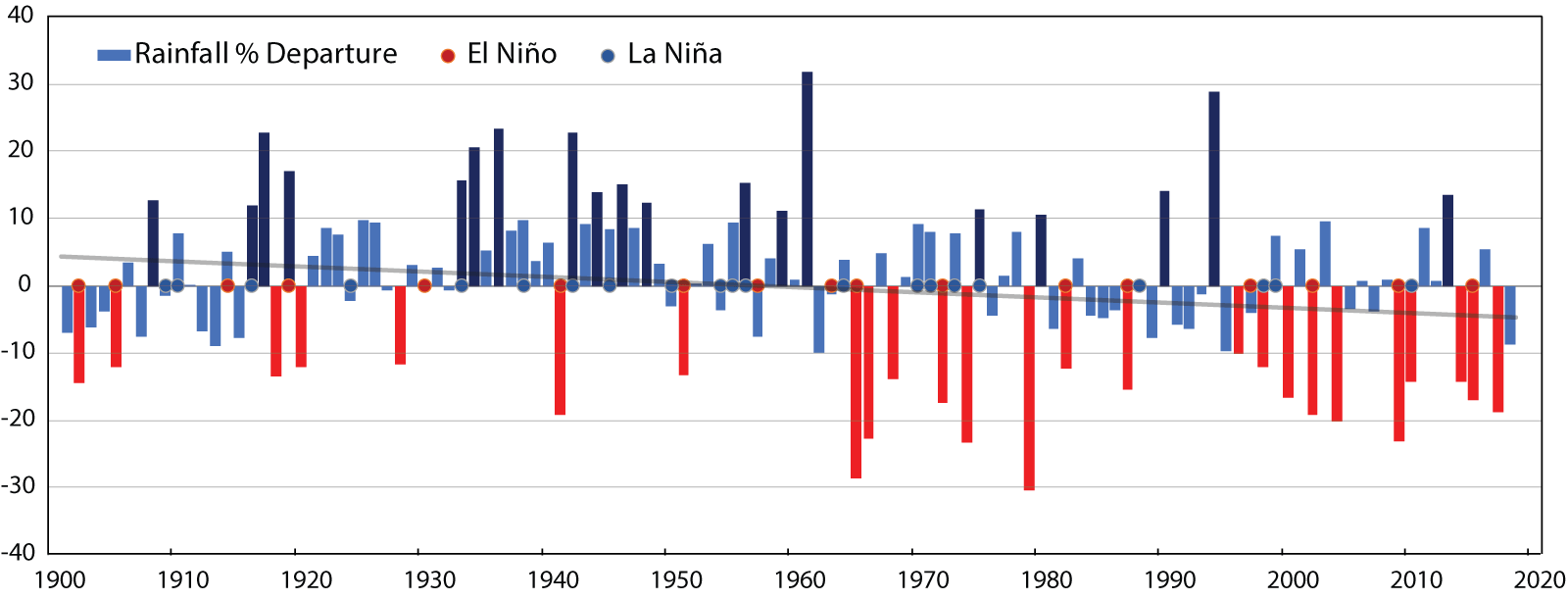
The figure above shows the percentage departure of summer monsoon rainfall over central India (76-86°E, 19-26°N) during 1901-2018. Drought years (below -10% departure) are marked in red color and flood years (above 10% departure) are marked in dark blue color. El Niño and La Niña conditions for the summer season are marked using red and blue dots.
Ref: Singh, D., S. Ghosh, M. K. Roxy and S. McDermid, 2019: Indian summer monsoon: Extreme events, historical changes, and role of anthropogenic forcings. WIREs Clim Change. 2019;10:e571, doi:10.1002/wcc.571.