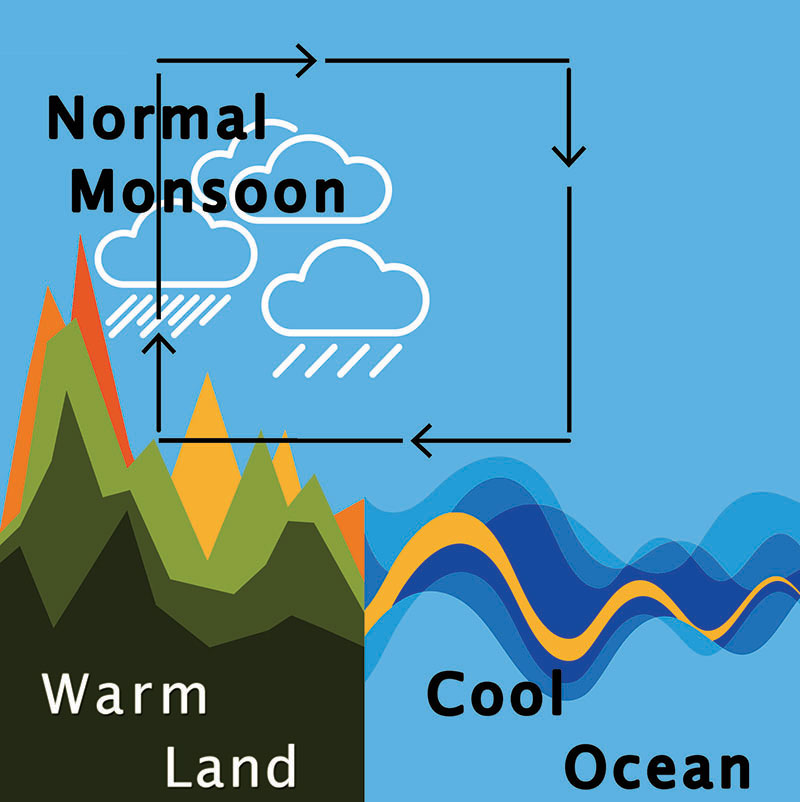
Monsoon is a term usually used to refer the seasonally changing rain-bearing winds, which affects the Indian subcontinent. The monsoon winds are caused by the extreme heating or cooling of the landmasses, in relation to the surrounding seas.
During the northern summer by the end of May, the Indian landmass gets relatively warmer than the Indian Ocean. This results in the onset of the southwesterly monsoon winds, which brings moisture from the Indian Ocean and pours it over the land. Once the rain lashes over the land, it cools but the latent heat released into the atmosphere keeps the meridional thermal contrast functional in the troposphere.
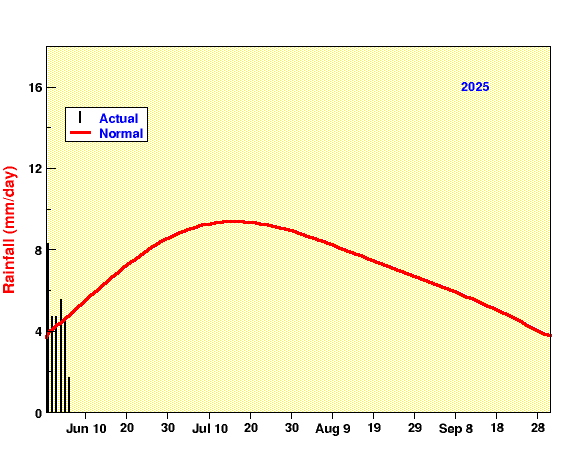
The summer monsoon during June-September provides 80-90% of the total rainfall over the Indian subcontinent.